IEEE 14th Image, Video, and Multidimensional Signal Processing Workshop (IVMSP 2022)
June 26-29, 2022 | Nafplio, Greece
Conference Website
[PDF][Slides][Video]
Ekrem Çetinkaya (Christian Doppler Laboratory ATHENA, Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Minh Nguyen (Christian Doppler Laboratory ATHENA, Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), and Christian Timmerer (Christian Doppler LaboratoryATHENA, Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt)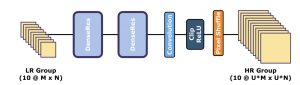
Abstract: Video is now an essential part of the Internet. The increasing popularity of video streaming on mobile devices and the improvement in mobile displays brought together challenges to meet user expectations. Advancements in deep neural networks have seen successful applications on several computer vision tasks such as super-resolution (SR). Although DNN-based SR methods significantly improve over traditional methods, their computational complexity makes them challenging to apply on devices with limited power, such as smartphones. However, with the improvement in mobile hardware, especially GPUs, it is now possible to use DNN based solutions, though existing DNN based SR solutions are still too complex. This paper proposes LiDeR, a lightweight video SR network specifically tailored toward mobile devices. Experimental results show that LiDeR can achieve competitive SR performance with state-of-the-art networks while improving the execution speed significantly, i.e., 267 % for X4 upscaling and 353 % for X2 upscaling compared to ESPCN.
Keywords: Super-resolution, Mobile machine learning, Video super-resolution.

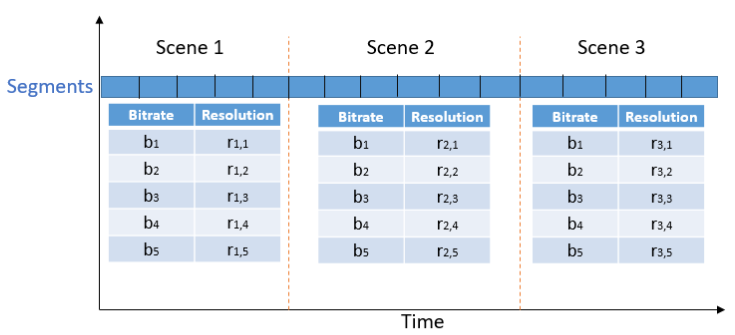
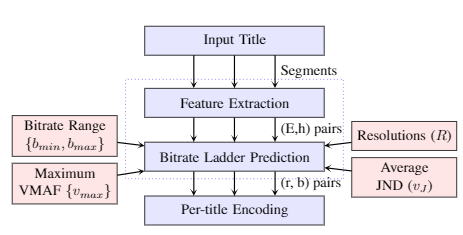
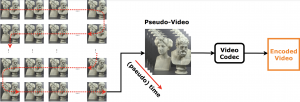


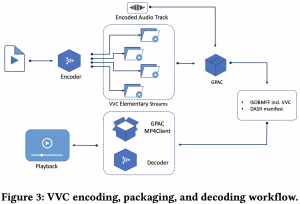 Abstract: There exist many applications that produce multimedia traffic over the Internet. Video streaming is on the list, with a rapidly growing desire for more bandwidth to deliver higher resolutions such as Ultra High Definition (UHD) 8K content. HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) technique defines baselines for audio-visual content streaming to balance the delivered media quality and minimize streaming session defects. On the other hand, video codecs development and standardization help the theorem by introducing efficient algorithms and technologies. Versatile Video Coding (VVC) is one of the latest advancements in this area that is still not fully optimized and supported on all platforms. Stated optimization and supporting many platforms require years of research and development. This paper offers a dataset that facilitates the research and development of the aforementioned technologies. Our open-source dataset comprises Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) multimedia test assets of encoded Advanced Video Coding (AVC), High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), AOMedia Video 1 (AV1), and VVC content with resolutions of up to 7680×4320 or 8K. Our dataset has a maximum media duration of 322 seconds, and we offer our MPEG-DASH packaged content with two segments lengths, 4 and 8 seconds.
Abstract: There exist many applications that produce multimedia traffic over the Internet. Video streaming is on the list, with a rapidly growing desire for more bandwidth to deliver higher resolutions such as Ultra High Definition (UHD) 8K content. HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) technique defines baselines for audio-visual content streaming to balance the delivered media quality and minimize streaming session defects. On the other hand, video codecs development and standardization help the theorem by introducing efficient algorithms and technologies. Versatile Video Coding (VVC) is one of the latest advancements in this area that is still not fully optimized and supported on all platforms. Stated optimization and supporting many platforms require years of research and development. This paper offers a dataset that facilitates the research and development of the aforementioned technologies. Our open-source dataset comprises Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) multimedia test assets of encoded Advanced Video Coding (AVC), High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), AOMedia Video 1 (AV1), and VVC content with resolutions of up to 7680×4320 or 8K. Our dataset has a maximum media duration of 322 seconds, and we offer our MPEG-DASH packaged content with two segments lengths, 4 and 8 seconds.











