Adaptive Compressed Domain Video Encryption
Expert Systems With Applications
[PDF]
Mohammad Ghasempour (AAU, Austria), Yuan Yuan (Southwest Jiaotong University), Hadi Amirpour (AAU, Austria), Hongjie He (Southwest Jiaotong University), and Christian Timmerer (AAU, Austria)
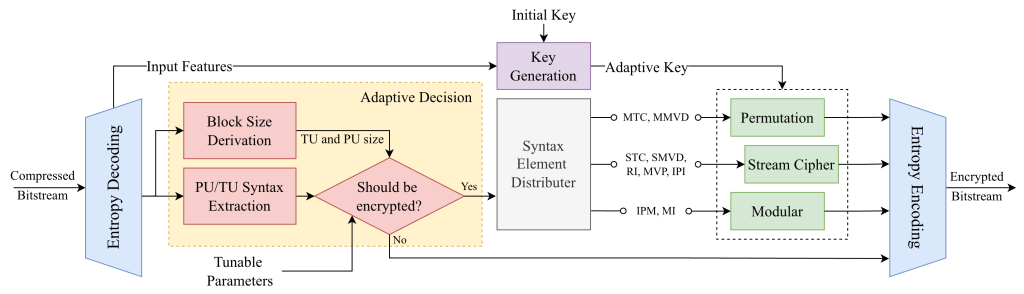
Abstract: With the ever-increasing amount of digital video content, efficient encryption is crucial to protect visual content across diverse platforms. Existing methods often incur excessive bitrate overhead due to content variability. Furthermore, since most videos are already compressed, encryption in the compressed domain is essential to avoid processing overhead and re-compression quality loss. However, achieving both format compliance and compression efficiency while ensuring that the decoded content remains unrecognizable is challenging in the compressed domain, since only limited information is available without full decoding. This paper proposes an adaptive compressed domain video encryption (ACDC) method that dynamically adjusts the encryption strategy according to content characteristics. Two tunable parameters derived from the bitstream information enable adaptation to various application requirements. An adaptive syntax integrity method is employed to produce format-compliant bitstreams without full decoding. Experimental results show that ACDC reduces bitrate overhead by 48.2% and achieves a 31-fold speedup in encryption time compared to the latest state of the art, while producing visually unrecognizable outputs.