May 7-10, 2023 | Denver, US
[PDF] [Slides]
Vignesh V Menon (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Reza Farahani (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), Prajit T Rajendran (Universite Paris-Saclay), Mohammed Ghanbari (University of Essex), Hermann Hellwagner (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt).
Abstract:
In recent years, video streaming applications have proliferated the demand for Video Quality Assessment (VQA). Reduced reference video quality assessment (RR-VQA) is a category of VQA where certain features (e.g., texture, edges) of the original video are provided for quality assessment. It is a popular research area for various applications such as social media, online games, and video streaming. This paper introduces a reduced reference Transcoding Quality Prediction Model (TQPM) to determine the visual quality score of the video possibly transcoded in multiple stages. The quality is predicted using Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-energy-based features of the video (i.e., the video’s brightness, spatial texture information, and temporal activity) and the target bitrate representation of each transcoding stage. To do that, the problem is formulated, and a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-based quality prediction model is presented. Experimental results illustrate that, on average, TQPM yields PSNR, SSIM, and VMAF predictions with an ?2 score of 0.83, 0.85, and 0.87, respectively, and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 1.31 dB, 1.19 dB, and 3.01, respectively, for single-stage transcoding.
Furthermore, an ?2 score of 0.84, 0.86, and 0.91, respectively, and MAE of 1.32 dB, 1.33 dB, and 3.25, respectively, are observed for a two-stage transcoding scenario. Moreover, the average processing time of TQPM for 4s segments is 0.328s, making it a practical VQA method in online streaming applications.
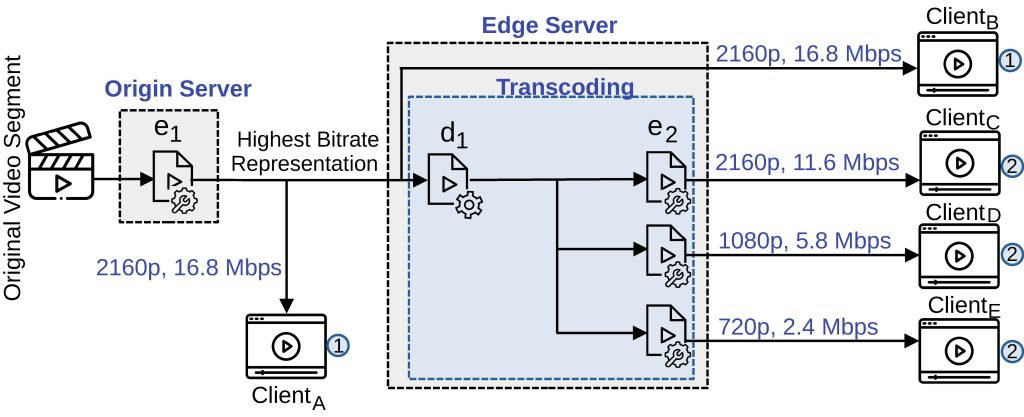
An example scenario of VQA in adaptive streaming applications.