IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM)
December 4-8, 2022 |Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
[PDF][Slides]
Reza Farahani (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Abdelhak Bentaleb (National University of Singapore, Singapore), Ekrem Cetinkaya (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Roger Zimmermann (National University of Singapore, Singapore), and Hermann Hellwagner (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria)
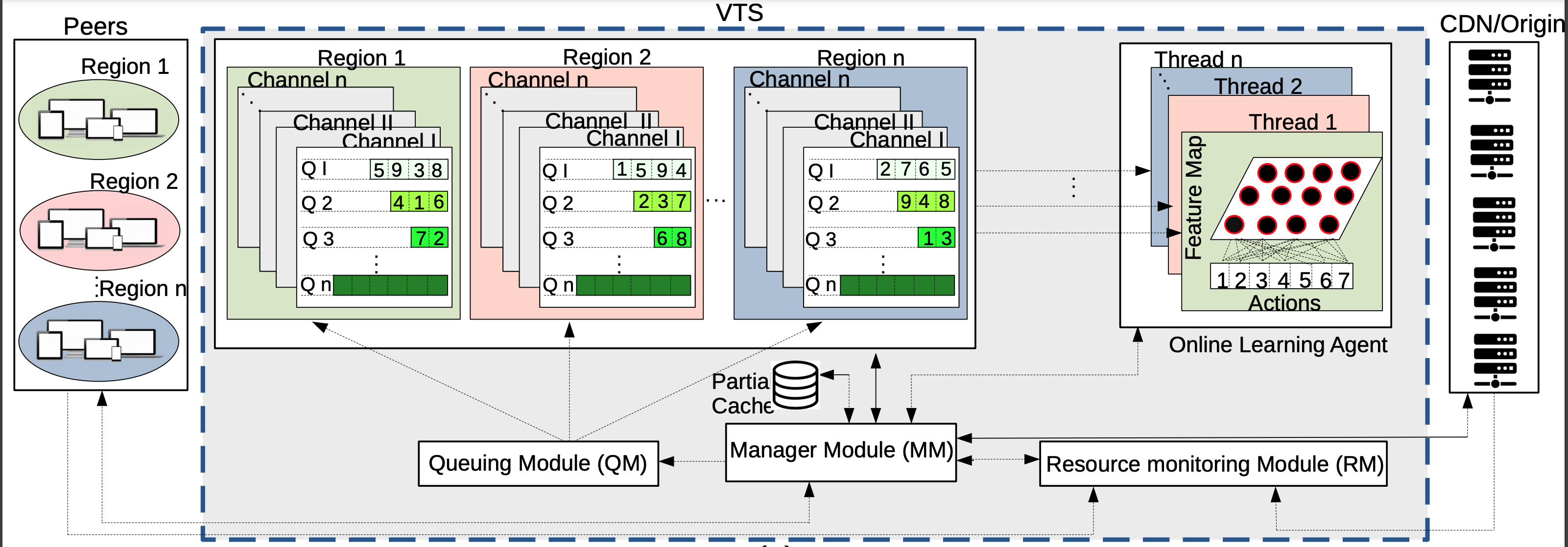
Abstract: a cost-effective, scalable, and flexible architecture that supports low latency and high-quality live video streaming is still a challenge for Over-The-Top (OTT) service providers. To cope with this issue, this paper leverages Peer-to-Peer (P2P), Content Delivery Network (CDN), edge computing, Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and distributed video transcoding paradigms to introduce a hybRId P2P-CDN arcHiTecture for livE video stReaming (RICHTER). We first introduce RICHTER’s multi-layer architecture and design an action tree that considers all feasible resources provided by peers, edge, and CDN servers for serving peer requests with minimum latency and maximum quality. We then formulate the problem as an optimization model executed at the edge of the network. We present an Online Learning (OL) approach that leverages an unsupervised Self Organizing Map (SOM) to (i) alleviate the time complexity issue of the optimization model and (ii) make it a suitable solution for large-scale scenarios by enabling decisions for groups of requests instead of for single requests. Finally, we implement the RICHTER framework, conduct our experiments on a large-scale cloud-based testbed including 350 HAS players, and compare its effectiveness with baseline systems. The experimental results illustrate that RICHTER outperforms baseline schemes in terms of users’ Quality of Experience (QoE), latency, and network utilization, by at least 59%, 39%, and 70%, respectively.
Index Terms—HAS; Edge Computing; NFV; CDN; P2P; Low Latency; QoE; Video Transcoding; Online Learning.

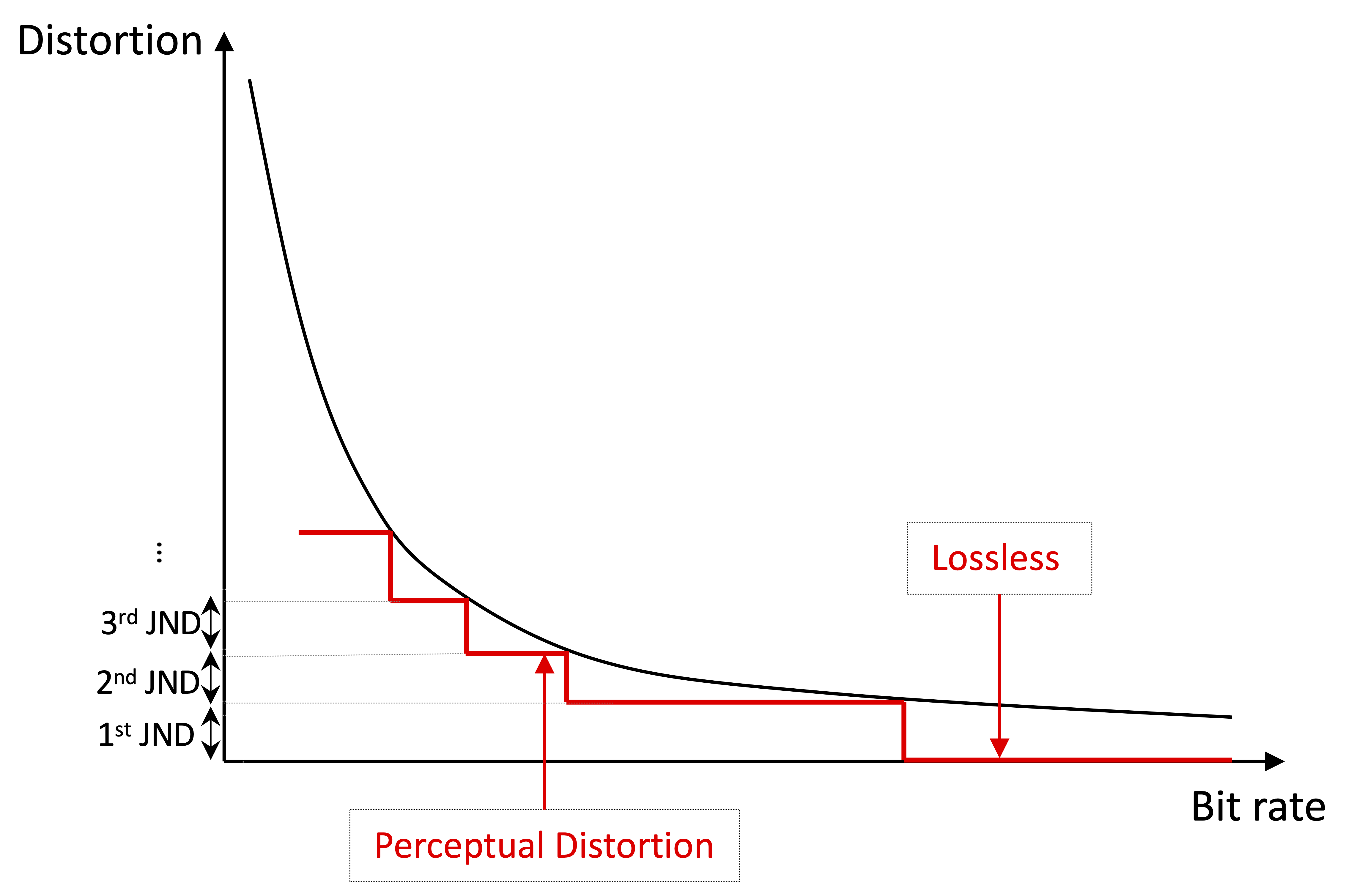 optimization and reduction of video delivery costs. Per-Title encoding, in contrast to a fixed bitrate ladder, shows significant promise to deliver higher quality video streams by addressing the trade-off between compression efficiency and video characteristics such as resolution and frame rate.
optimization and reduction of video delivery costs. Per-Title encoding, in contrast to a fixed bitrate ladder, shows significant promise to deliver higher quality video streams by addressing the trade-off between compression efficiency and video characteristics such as resolution and frame rate.

 Abstract: In general, manipulated videos will eventually undergo recompression. Video transcoding will occur when the standard of recompression is different from the prior standard. Therefore, as a special sign of recompression, video transcoding can also be considered evidence of forgery in video forensics. In this paper, we focus on the detection and localization of video transcoding from AVC to HEVC (AVC-HEVC). There are two probable cases of AVC-HEVC transcoding – whole video transcoding and partial frame transcoding. However, the existing forensic methods only consider the detection of whole video transcoding, and they do not consider partial frame transcoding localization. In view of this, we propose a framewise scheme based on a convolutional neural network. First, we analyze that the essential difference between AVC-HEVC and HEVC is reflected in the high-frequency components of decoded frames. Then, the partition and location information of prediction units (PUs) are introduced to generate frame-level PU maps to make full use of the local artifacts of PUs. Finally, taking the decoded frames and PU maps as inputs, a dual-path network including specific convolutional modules and an adaptive fusion module is proposed. Through it, the artifacts on a single frame can be better extracted, and the transcoded frames can be detected and localized. Coupled with a simple voting strategy, the results of whole transcoding detection can be easily obtained. A large number of experiments are conducted to verify the performances. The results show that the proposed scheme outperforms or rivals the state-of-the-art methods in AVC-HEVC transcoding detection and localization.
Abstract: In general, manipulated videos will eventually undergo recompression. Video transcoding will occur when the standard of recompression is different from the prior standard. Therefore, as a special sign of recompression, video transcoding can also be considered evidence of forgery in video forensics. In this paper, we focus on the detection and localization of video transcoding from AVC to HEVC (AVC-HEVC). There are two probable cases of AVC-HEVC transcoding – whole video transcoding and partial frame transcoding. However, the existing forensic methods only consider the detection of whole video transcoding, and they do not consider partial frame transcoding localization. In view of this, we propose a framewise scheme based on a convolutional neural network. First, we analyze that the essential difference between AVC-HEVC and HEVC is reflected in the high-frequency components of decoded frames. Then, the partition and location information of prediction units (PUs) are introduced to generate frame-level PU maps to make full use of the local artifacts of PUs. Finally, taking the decoded frames and PU maps as inputs, a dual-path network including specific convolutional modules and an adaptive fusion module is proposed. Through it, the artifacts on a single frame can be better extracted, and the transcoded frames can be detected and localized. Coupled with a simple voting strategy, the results of whole transcoding detection can be easily obtained. A large number of experiments are conducted to verify the performances. The results show that the proposed scheme outperforms or rivals the state-of-the-art methods in AVC-HEVC transcoding detection and localization. Hadi Amirpour is a postdoc research fellow at ATHENA directed by Prof. Christian Timmerer. He received his B.Sc. degrees in Electrical and Biomedical Engineering, and he pursued his M.Sc. in Electrical Engineering. He got his Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Klagenfurt in 2022. He was appointed co-chair of Task Force 7 (TF7) Immersive Media Experience (IMEx) at the 15th Qualinet meeting. He was involved in the project EmergIMG, a Portuguese consortium on emerging imaging technologies, funded by the Portuguese funding agency and H2020. Currently, he is working on the ATHENA project in cooperation with its industry partner Bitmovin. His research interests are image processing and compression, video processing and compression, quality of experience, emerging 3D imaging technology, and medical image analysis.
Hadi Amirpour is a postdoc research fellow at ATHENA directed by Prof. Christian Timmerer. He received his B.Sc. degrees in Electrical and Biomedical Engineering, and he pursued his M.Sc. in Electrical Engineering. He got his Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Klagenfurt in 2022. He was appointed co-chair of Task Force 7 (TF7) Immersive Media Experience (IMEx) at the 15th Qualinet meeting. He was involved in the project EmergIMG, a Portuguese consortium on emerging imaging technologies, funded by the Portuguese funding agency and H2020. Currently, he is working on the ATHENA project in cooperation with its industry partner Bitmovin. His research interests are image processing and compression, video processing and compression, quality of experience, emerging 3D imaging technology, and medical image analysis.











