Improving the Efficiency of VVC using Partitioning of Reference Frames
The IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (IEEE ISCAS 2025)
25–28 May 2025 // London, United Kingdom
[PDF]
Kamran Qureshi (AAU, Austria), Hadi Amirpour (AAU, Austria), Christian Timmerer (AAU, Austria)
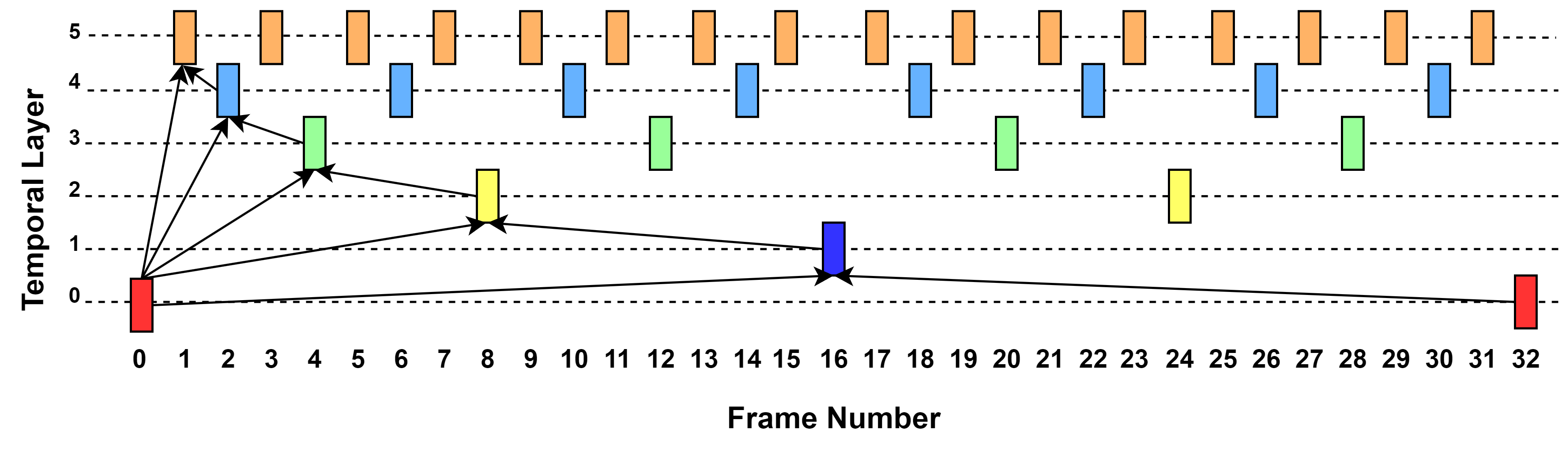
Abstract: In response to the growing demand for high-quality videos, a new coding standard, Versatile Video Coding (VVC), was released in 2020. VVC is based on the same hybrid coding architecture as its predecessor, High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), providing a bitrate reduction of approximately 50% for the same subjective quality. VVC extends HEVC’s Coding Tree Unit (CTU) partitioning with more flexible block sizes, increasing its encoding complexity. Optimization is essential to making efficient use of VVC in practical applications. VVenC, an optimized open-source VVC encoder, introduces multiple presets to address the trade-off between compression efficiency and encoder complexity. Although an optimized set of encoding tools has been selected for each preset, the rate-distortion (RD) search space in the encoder presets still poses a challenge for efficient encoder implementations. This paper proposes Early Termination using Reference Frames (ETRF). It improves the trade-off between encoding efficiency and time complexity and positions itself as a new preset between medium and fast presets. The CTU partitioning map of the reference frames present in lower temporal layers is employed to accelerate the encoding of frames in higher temporal layers. The results show a reduction in the encoding time of around 22% compared to the medium preset. Specifically, for videos with high spatial and temporal complexities, which typically require longer encoding times, the proposed method shows an improved BDBR/BDT compared to the fast preset.