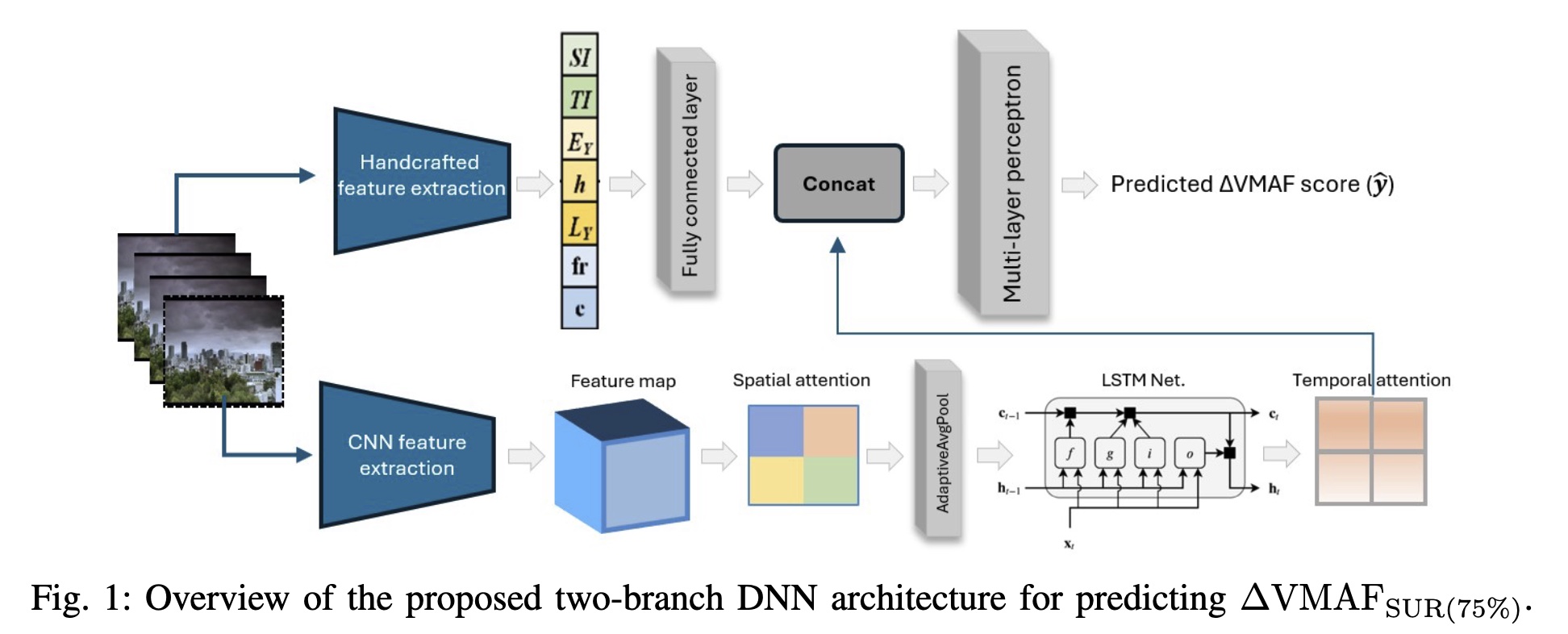
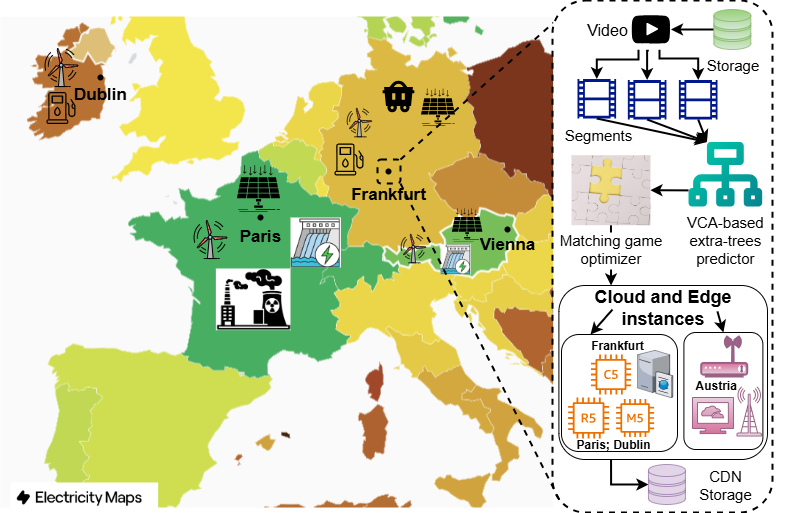
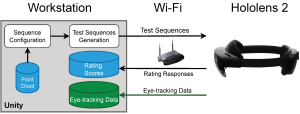
Perceptual JND Prediction for VMAF Using Content-Adaptive Dual-Path Attention
IEEE VCIP 2025
December 1 – December 4, 2025
Klagenfurt, Austria
[PDF]
Milad Ghanbari (AAU, Austria), Hadi Amirpour (AAU, Austria), Christian Timmerer (AAU, Austria), M.H. Izadimehr (AAU, Austria), Wei Zhou (Cardiff University, UK), Cosmin Stejerean (Meta, US)
Abstract: This paper presents a block stacking simulation developed for Apple Vision Pro (AVP) using Unity’s PolySpatial framework, designed to study both depth perception in spatial computing and physics comprehension of user-driven kinetic controls in augmented reality (AR). The simulation offers two interactive modes: a tower assembly mode and a removal mode. Each game session includes four stages with the virtual table positioned at various distances to observe user adaptation across varying virtual depths. User input is captured through eye tracking and hand tracking, and block behavior is handled by real-time physics simulation, which includes collision response, gravity, and mass-based interactions. The system supports two physics configurations: raw Unity physics and a modified variant with adjusted material and rigidbody parameters for improved stability and realism. It utilizes spatial computing features such as world anchoring to preserve spatial consistency and depth perception through stereoscopic rendering and dynamic shadows, so that users can better judge the spatial coordinates between virtual blocks and their physical surroundings. The simulation is intended to evaluate how 3D spatial rendering and physically realistic interactions contribute to immersion and task performance in AR environments. To assess user performance, the system records key interaction metrics to support analysis of learning progression, control accuracy, and adaptability across varying distances and physics configurations. This work contributes to the understanding of spatial and physics-based interaction design in AR and may inform future applications in education, simulation, and spatial gaming.