IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP)
[PDF]
Hadi Amirpour (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Christine Guillemot (INRIA, France), Mohammad Ghanbari (University of Essex, UK), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria)
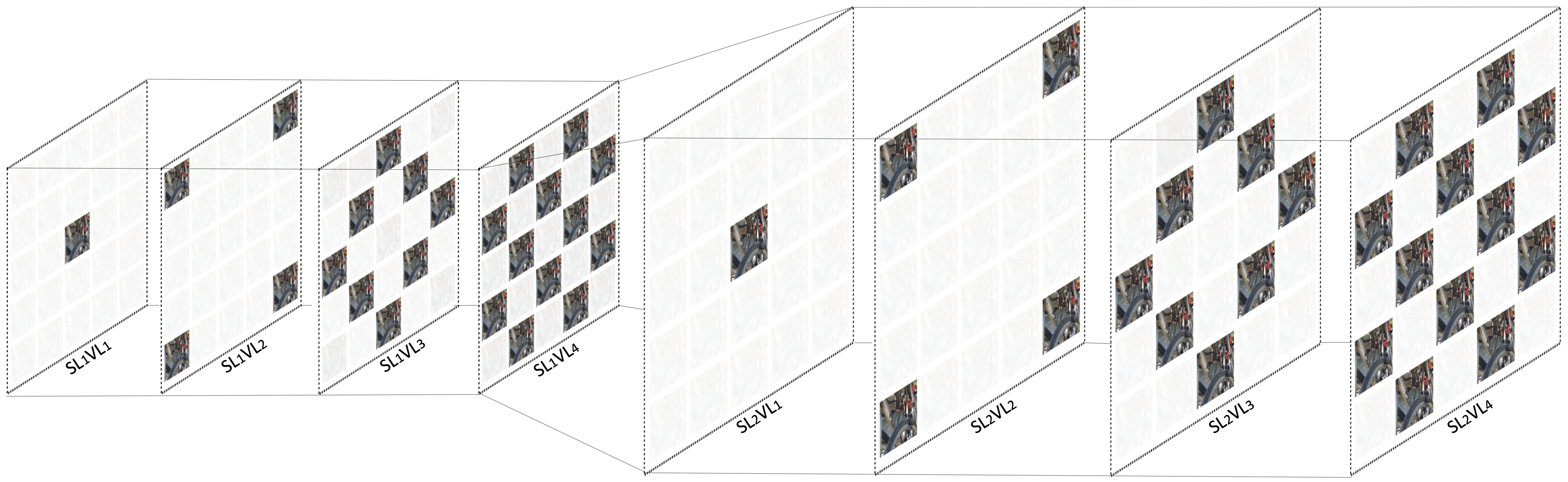
Abstract: Light field imaging, which captures both spatial and angular information, improves user immersion by enabling post-capture actions, such as refocusing and changing view perspective. However, light fields represent very large volumes of data with a lot of redundancy that coding methods try to remove. State-of-the-art coding methods indeed usually focus on improving compression efficiency and overlook other important features in light field compression such as scalability. In this paper, we propose a novel light field image compression method that enables (i) viewport scalability, (ii) quality scalability, (iii) spatial scalability, (iv) random access, and (v) uniform quality distribution among viewports, while keeping compression efficiency high. To this end, light fields in each spatial resolution are divided into sequential viewport layers, and viewports in each layer are encoded using the previously encoded viewports. In each viewport layer, the available viewports are used to synthesize intermediate viewports using a video interpolation deep learning network. The synthesized views are used as virtual reference images to enhance the quality of intermediate views. An image super-resolution method is applied to improve the quality of the lower spatial resolution layer. The super-resolved images are also used as virtual reference images to improve the quality of the higher spatial resolution layer.
The proposed structure also improves the flexibility of light field streaming, provides random access to the viewports, and increases error resiliency. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a high compression efficiency and it can adapt to the display type, transmission channel, network condition, processing power, and user needs.
Keywords—Light field, compression, scalability, random access, deep learning.