Klagenfurt, January 15, 2024
Congratulations to Dr. Vignesh V Menon for successfully defending his dissertation on “Content-adaptive Video Coding for HTTP Adaptive Streaming” at Universität Klagenfurt in the context of the Christian Doppler Laboratory ATHENA.

Abstract
In today’s dynamic streaming landscape, where viewers access content on various devices and en- counter fluctuating network conditions, optimizing video delivery for each unique scenario is imperative. Video content complexity analysis, content-adaptive video coding, and multi-encoding methods are fundamental for the success of adaptive video streaming, as they serve crucial roles in delivering high-quality video experiences to a diverse audience. Video content complexity analysis allows us to comprehend the video content’s intricacies, such as motion, texture, and detail, providing valuable insights to enhance encoding decisions. By understanding the content’s characteristics, we can efficiently allocate bandwidth and encoding resources, thereby improving compression efficiency without compromising quality. Content-adaptive video coding techniques built upon this analysis involve dynamically adjusting encoding parameters based on the content complexity. This adaptability ensures that the video stream remains visually appealing and artifacts are minimized, even under challenging network conditions. Multi-encoding methods further bolster adaptive streaming by offering faster encoding of multiple representations of the same video at different bitrates. This versatility reduces computational overhead and enables efficient resource allocation on the server side. Collectively, these technologies empower adaptive video streaming to deliver optimal visual quality and uninterrupted viewing experiences, catering to viewers’ diverse needs and preferences across a wide range of devices and network conditions. Embracing video content complexity analysis, content-adaptive video coding, and multi-encoding methods is essential to meet modern video streaming platforms’ evolving demands and create immersive experiences that captivate and engage audiences. In this light, this dissertation proposes contributions categorized into four classes:
Video complexity analysis: For the online analysis of video content complexity, selecting low- complexity features is critical to ensure low-latency video streaming without disruptions. The spatial information (SI) and temporal information (TI) are state-of-the-art spatial and temporal complexity features. However, these features are not optimized for online analysis in live-streaming applications. Moreover, the correlation of the features to the video coding parameters like bitrate and encoding time is not significant. This thesis proposes discrete cosine transform (DCT)-energy-based spatial and temporal complexity features to overcome these limitations and provide an efficient video com- plexity analysis regarding accuracy and speed for every video (segment). The proposed features are determined at an average rate of 370 frames per second for ultra high definition (UHD) video content and used in estimating encoding parameters online.
Content-adaptive encoding optimizations: Content-adaptive encoding algorithms enable bet- ter control of codec-specific parameters and mode decisions inside the encoder to achieve higher bitrate savings and/or save encoding time. The contributions of this class are listed as follows:
- A scene detection algorithm is proposed using the video complexity analysis features. The proposed algorithm yields a true positive rate of 78.26% and a false positive rate of 0.01%, compared to the state-of-the-art algorithm’s true positive rate of 53.62% and false positive rate of 0.03%.
- An intra coding unit depth prediction (INCEPT) algorithm is proposed, which limits rate- distortion optimization for each coding tree unit (CTU) in high efficiency video coding (HEVC) by utilizing the spatial correlation with the neighboring CTUs, which is computed using the luma texture complexity feature introduced in the first contribution class. Experimental results show that INCEPT achieves a 23.24% reduction in the overall encoding time with a negligible loss in compression efficiency.
Online per-title encoding optimizations: Per-title encoding has gained attraction over recent years in adaptive streaming applications. Each video is segmented into multiple scenes, and optimal encoding parameters are selected. The contributions in this category are listed as follows:
- Online resolution prediction scheme (ORPS), which predicts optimized resolution using the video content complexity of the video segment and the predefined set of target bitrates, is proposed. ORPS yields an average bitrate reduction of 17.28% and 22.79% for the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, compared to the standard HTTP live streaming (HLS) bitrate ladder using x265 constant bitrate (CBR) encoding.
- Online framerate prediction scheme (OFPS) is proposed to predict optimized framerate using the video content complexity of the video segment and the predefined set of target bitrates. OFPS yields an average bitrate reduction of 15.87% and 18.20% for the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, compared to the original framerate CBR encoding of UHD 120fps sequences using x265, accompanied by an overall encoding time reduction of 21.82%.
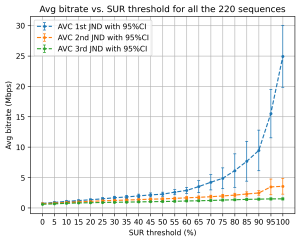
- Just noticeable difference (JND)-aware bitrate ladder prediction scheme (JBLS) is proposed, which predicts optimized bitrate-resolution pairs such that there is a perceptual quality differ- ence of one JND between representations. An average bitrate reduction of 12.94% and 17.94% for the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, is observed, compared to the HLS CBR bitrate ladder encoding using x265. For a target JND of 6 VMAF points, JBLS achieves a storage reduction of 42.48% and 25.35% reduction in encoding time.
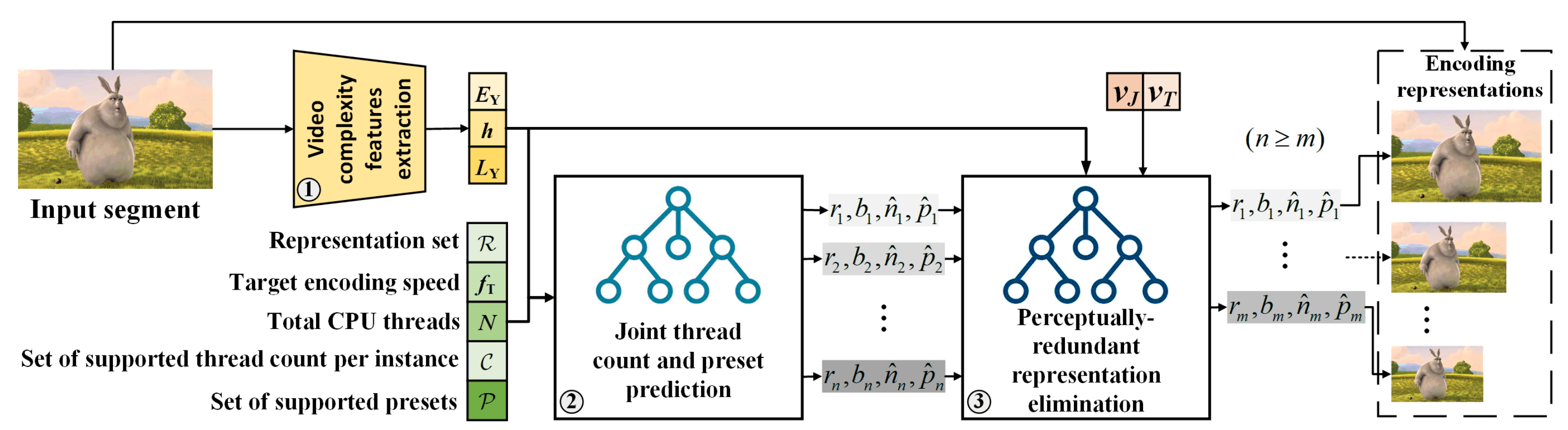
- Online encoding preset prediction scheme (OEPS) is proposed, which predicts the optimized encoder preset based on the target bitrate, resolution, and video framerate for every video segment. OEPS yields consistent encoding speed across various representations with an overall quality improvement of 0.83 dB PSNR and 5.81 VMAF points with the same bitrate, compared to the fastest preset encoding of the HLS CBR bitrate ladder using x265.
- A JND-aware two-pass per-title encoding scheme, named live variable bitrate encoding (LiveVBR) is proposed, which predicts perceptually-aware bitrate-resolution-framerate-rate factor tuples for the bitrate ladder of each video segment. LiveVBR yields an average bitrate reduction of 18.80% and 32.59% for the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, compared to the HLS CBR bitrate ladder encoding using x265. For a target JND of six VMAF points, LiveVBR also resulted in a 68.96% reduction in storage space and an 18.58% reduction in encoding time, with a negligible impact on streaming latency.
Multi-encoding optimizations: Presently, most streaming services utilize cloud-based encoding techniques, enabling a fully parallel encoding process to reduce the overall encoding time. This dissertation comprehensively proposes various multi-rate and multi-encoding schemes in serial and parallel encoding scenarios. Furthermore, it introduces novel heuristics to limit the rate-distortion optimiza- tion (RDO) process across multiple representations. Based on these heuristics, three multi-encoding schemes are proposed, which rely on encoder analysis sharing across different representations: (i) optimized for the highest compression efficiency, (ii) optimized for the best compression efficiency- encoding time savings trade-off and (iii) optimized for the best encoding time savings. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed multi-encoding schemes (i), (ii), and (iii) reduce the overall serial encoding time by 34.71%, 45.27%, and 68.76% with a 2.3%, 3.1%, and 4.5% bitrate increase to maintain the same VMAF, respectively compared to stand-alone encodings. The overall parallel encoding time is reduced by 22.03%, 20.72%, and 76.82% compared to stand-alone encodings for schemes (i), (ii), and (iii), respectively.
Slides available here: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshows/contentadaptive-video-coding-for-http-adaptive-streaming/265462304