The Christian Doppler (CD) Laboratory ATHENA was established in October 2019 to tackle current and future research and deployment challenges of HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) and emerging streaming methods. The goal of CD laboratories is to conduct application-oriented basic research, promote collaboration between universities and companies, and facilitate technology transfer. They are funded through a public-private partnership between companies and the Christian Doppler Research Association, which is funded by the Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs and the National Foundation for Research, Technology, and Development (Nationalstiftung für Forschung, Technologie und Entwicklung (FTE)). ATHENA is supported by Bitmovin as a company partner.
The CD laboratories have a duration of seven years and undergo rigorous scientific review after two and five years. This spring, the CD lab ATHENA completed its 5-year evaluation, and we have just received official notification from the CDG that we have successfully passed the review. Consequently, it is time to briefly outline the main achievements during this second phase (i.e., years 2 to 5) of the CD lab ATHENA.
Before exploring the achievements, it’s important to highlight the ongoing relevance of research in video streaming, given its dominance in today’s Internet usage. The January 2024 Sandvine Internet Phenomena report revealed that video streaming accounts for 68% of fixed/wired Internet traffic and 64% for mobile Internet traffic. Specifically, Video on Demand (VoD) represents 54% of fixed/wired and 57% of mobile traffic, while live streaming contributes to 14% of fixed/wired and 7% of mobile traffic. The major services in this domain include YouTube and Netflix, each commanding more than 10% of the overall Internet traffic, with TikTok, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ also playing significant roles.
ATHENA is structured into four work packages, each with distinct objectives as detailed below:
- Content provisioning: Primarily involves video encoding for HAS, quality-aware encoding, learning-based encoding, and multi-codec HAS.
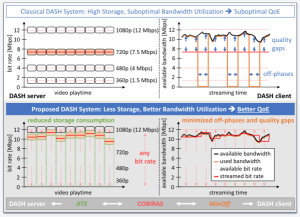
- Content delivery: Addresses HAS issues by utilizing edge computing, exchanging information between CDN/SDN and clients, providing network assistance for clients, and evaluating corresponding utilities.
- Content consumption: Focuses on bitrate adaptation schemes, playback improvements, context and user awareness, and studies on Quality of Experience (QoE).
- End-to-end aspects: Offers a comprehensive view of application and transport layer enhancements, Quality of Experience (QoE) models, low-latency HAS, and learning-based HAS.
During the 2nd phase of ATHENA’s work, we achieved significant results, including publications in respected academic journals and conferences. Specifically, our publications were featured in key multimedia, signal processing, computer networks & wireless communication, and computing systems venues, as categorized by Google Scholar under engineering and computer science. Some of the notable publications include IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials (impact factor: 35.6), IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (10.6), IEEE Internet of Things Journal (10.6), IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (8.4), and IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (7.3).
Furthermore, we focused on technology transfer by submitting 16 invention disclosures, resulting in 13 patent applications (including provisionals). Collaborating with our company partner, we obtained 6 granted patents. Additionally, we’re pleased to report on the progress of our spin-off projects, as well as the funding secured for two FFG-funded projects named APOLLO and GAIA, and an EU Horizon Europe-funded innovation action called SPIRIT.
The ATHENA team was also active in organizing scientific events such as workshops, special sessions, and special issues at IEEE ICME, ACM MM, ACM MMSys, ACM CoNEXT, IEEE ICIP, PCS, and IEEE Network. We also contributed to reproducibility in research through open source tools (e.g., Video Complexity Analyzer and LLL-CAdViSE) and datasets (e.g., Video Complexity Dataset and Multi-Codec Ultra High Definition 8K MPEG-DASH Dataset) among others.
We also note our contributions to the applications of AI in video coding & streaming, for example in video coding and video streaming as follows:
- Fast Multi-Rate Encoding with Machine Learning (using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs))
- LiDeR: Lightweight video Super Resolution for mobile devices (using Deep Neural Networks (DNNs))
- Blind Visual Quality Assessment Using Vision Transformers
- Video Complexity Analysis (VCA) and optimizations for per-title encoding (using Linear Regression, Random Forest, and XGBoost models)
- DeepStream: Video streaming enhancements using compressed deep neural networks (using Deep Neural Networks (DNNs))
- ECAS-ML: Edge-assisted adaptive bitrate switching (using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM))
- Quality Optimization of Live Streaming Services over HTTP with Reinforcement Learning (RL)
A major outcome of the second phase is the successful defense of the inaugural cohort of PhD students:
- Dr. Alireza Erfanian: “Optimizing QoE and Latency of Video Streaming using Edge Computing and In-Network Intelligence”, May 25, 2023
- Dr. Ekrem Çetinkaya: “Video Coding Enhancements for HTTP Adaptive Streaming using Machine Learning”, June 7, 2023
- Dr. Minh Nguyen: “Policy-driven Dynamic HTTP Adaptive Streaming Player Environment”, June 30, 2023
- Dr. Jesús Aguilar Armijo: “Multi-access Edge Computing for Adaptive Video Streaming”, July 10, 2023
- Dr. Reza Farahani: “Network-Assisted Delivery of Adaptive Video Streaming Services through CDN, SDN, and MEC”, August 22, 2023
- Dr. Vignesh V Menon: “Content-adaptive Video Coding for HTTP Adaptive Streaming”, January 15, 2024
- Dr. Babak Taraghi, “End-to-end Quality of Experience Evaluation for HTTP Adaptive Streaming”, July 10, 2024
Two postdoctoral scholars have reached a significant milestone on their path toward habilitation
- Dr. Hadi Amirpour, “Video Coding for Efficient HTTP Adaptive Streaming”, February 8, 2024
- Dr. Farzad Tashtarian, “How to Optimize Dynamic Adaptive Video Streaming? Challenges and Solutions”, February 27, 2023 & “End-to-End Adaptive Video Streaming Optimization”, June 26, 2024
During the second phase, each work package produced excellent publications in their domain, briefly highlighted in the following. Content provisioning (WP-1) focuses mainly on video coding for HAS (43 papers) and immersive media coding for streaming (4 papers). The former can be further subdivided into the following topic areas:
- Video complexity: spatial and temporal feature extraction (4 papers)
- Compression efficiency improvement of individual representations (1 paper)
- Encoding parameter prediction for HAS (9 papers)
- Efficient bitrate ladder construction (4 papers)
- Fast multi-rate encoding (3 papers)
- Data security and data hiding (7 papers)
- Energy-efficient video encoding for HAS (4 papers)
- Advancing video quality evaluation (7 papers)
- Datasets (4 papers)
Content delivery (WP-2) dealt with SDN/CDN assistance for HAS, edge computing support for HAS, and network-embedded media streaming support, resulting in 21 papers. Content consumption (WP-3) worked on QoE enhancement mechanisms at client-side and QoE- and energy-aware content consumption (11 papers). Finally, end-to-end Aspects (WP-4) produced 15 papers in the area of end-to-end QoE improvement in multimedia video streaming. We reported 94 papers published/accepted for the ATHENA 5-year evaluation.
In this context, it is also important to highlight the collaboration within ATHENA, which has resulted in joint publications across various work packages (WPs) and with other ITEC members. For example, collaborations with Prof. Schöffmann (FWF-funded project OVID), FFG-funded projects APOLLO/GAIA, and EU-funded project SPIRIT. In addition, we would like to acknowledge our international collaborators, such as Prof. Hongjie He from Southwest Jiaotong University, Prof. Patrick Le Callet from the University of Nantes, Prof. Wassim Hamidouche from the Technology Innovation Institute (UAE), Dr. Sergey Gorinsky from IMDEA, Dr. Abdelhak Bentaleb from Concordia University, Dr. Raimund Schatz from AIT, and Prof. Pablo Cesar from CWI. We are also pleased to report the successful technology transfers to Bitmovin, particularly CAdViSE (WP-4) and WISH ABR (WP-3). Regular “Fun with ATHENA” meetups and Break-out Groups are utilized for in-depth discussions about innovations and potential technology transfers.
Over the next two years, the ATHENA project will prioritize the development of deep neural network/AI-based image and video coding within the context of HAS. This includes energy- and cost-aware video coding for HAS, immersive video coding such as volumetric video and holography, as well as Quality of Experience (QoE) and energy-aware content consumption for HAS (including energy-efficient, AI-based live video streaming) and generative AI for HAS.
Thanks to all current and former ATHENA team members: Samira Afzal, Hadi Amirpour, Jesús Aguilar Armijo, Emanuele Artioli, Christian Bauer, Alexis Boniface, Ekrem Çetinkaya, Reza Ebrahimi, Alireza Erfanian, Reza Farahani, Mohammad Ghanbari (late), Milad Ghanbari, Mohammad Ghasempour, Selina Zoë Haack, Hermann Hellwagner, Manuel Hoi, Andreas Kogler, Gregor Lammer, Armin Lachini, David Langmeier, Sandro Linder, Daniele Lorenzi, Vignesh V Menon, Minh Nguyen, Engin Orhan, Lingfeng Qu, Jameson Steiner, Nina Stiller, Babak Taraghi, Farzad Tashtarian, Yuan Yuan, and Yiying Wei. Finally, thanks to ITEC support staff Martina Steinbacher, Nina Stiller, Margit Letter, Marion Taschwer, and Rudolf Messner.
We also would like to thank the Christian Doppler Research Association for continuous support, organizing the review, and the reviewer for constructive feedback!



 Biography: Christian Timmerer is a full professor of computer science at Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt (AAU), Institute of Information Technology (ITEC) and he is the director of the Christian Doppler (CD) Laboratory ATHENA (
Biography: Christian Timmerer is a full professor of computer science at Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt (AAU), Institute of Information Technology (ITEC) and he is the director of the Christian Doppler (CD) Laboratory ATHENA (











